How to extract a column of a dataframe as a vector in R
In this tutorial, we will learn how to extract a column from a dataframe in R. We will extract a column as a vector using base R method and then see multiple examples of using dplyr’s pull() function to extract a column from a dataframe. 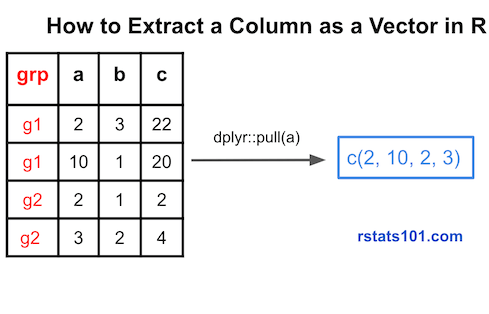 Extract A Column As Vector in R ### Getting Ready with Packages and Data Let us get started by loading tidyverse the suite of R packages.
Extract A Column As Vector in R ### Getting Ready with Packages and Data Let us get started by loading tidyverse the suite of R packages.
library(tidyverse)
# check the version of loaded package dplyr
packageVersion("dplyr")
## [1] '1.0.8'First, let us create a new toy dataframe with three columns using tibble() function. tibble() function creates a dataframe like object called tibble.
df %
mutate(id = row_number(),
counts = sample(1:20,6) )
df
## # A tibble: 6 × 3
## grp id counts
##
## 1 g2 1 1
## 2 g1 2 19
## 3 g1 3 12
## 4 g2 4 15
## 5 g1 5 7
## 6 g1 6 3Extract a column as vector in base R
To extract a column in base R, we use the dataframe name followed by $ symbol and then the column name of interest. In this example, we extract the column, counts, as a vector
df$counts
## [1] 7 5 16 13 11 18dplyr’s pull() function to extract a column as a vector
If we specify the column name as argument to pull() function, we will get the column as a vector.
df %>%
pull(counts)
## [1] 7 5 16 13 11 18dplyr’s pull() function to extract the last column as a vector
If we don’t specify any column of interest to dplyr’s pull() function, it will give the last column in the dataframe, ” (on the assumption that’s the column you’ve created most recently).”
df %>%
pull()
## [1] 1 19 12 15 7 3Extract a column as vector using dplyr’s pull() function with column position
We can also specify the position of a column to extract the column as vector. In the example below, we extract the third column from left as a vector from the dataframe by using pull(3) function.
df %>%
pull(3)
## [1] 1 19 12 15 7 3Extract a column as named vector using dplyr’s pull()
By providing two column names to pull() function, we can extract a column as a named vector with names from the second name argument to pull() function.
Here is an example, where we extract grp column as a named vector with names of the vector coming from second argument.
df %>%
pull(grp, counts)
## 1 19 12 15 7 3
## "g2" "g1" "g1" "g2" "g1" "g1"Here is an example, where we extract counts column as a named vector with names of the vector coming from “grp” column, a reverse of the previous example.
df %>%
pull(counts, grp)
## g2 g1 g1 g2 g1 g1
## 1 19 12 15 7 3